The Fundus Photograph Reading Center (FPRC) in the Department of Ophthalmology and Visual Sciences (DOVS) at the University of Wisconsin-Madison is the core imaging lab for a new international clinical study funded by the National Eye Institute, part of the National Institutes of Health, the nation’s medical research agency.
The AMD Ryan Initiative Study (ARIS) aims to understand the biology that drives the progression of age-related macular degeneration (AMD) so that therapies can be developed to halt its progression. In the ARIS study, investigators will examine 500 people over five years. This study will use the latest imaging technologies to visualize structures within the retina as well as novel tests of night vision and central vision to measure the participant’s visual function.
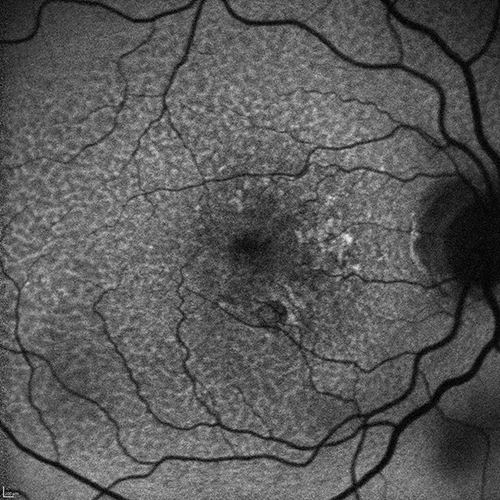
Amitha Domalpally, MD, research director of FPRC, commented, “The ARIS study is the first natural history study to understand the role of a specific feature of dry AMD called reticular pseudodrusen. FPRC will be performing detailed evaluation of drusen and reticular pseudodrusen using a multitude of new imaging technologies both to document early AMD and help develop novel markers in the eye that can predict progression. It is noteworthy that approximately 30 years ago, Dr. Ron Klein, Dr. Matthew Davis and Dr. Barbara Klein developed the Wisconsin Age-Related Maculopathy grading system which included reticular pseudodrusen as an additional phenotype. We are excited to advance the field further using the latest imaging systems such as quantitative autofluorescence, OCT angiography and ultrawide field imaging.”
SOURCE: National Institutes of Health